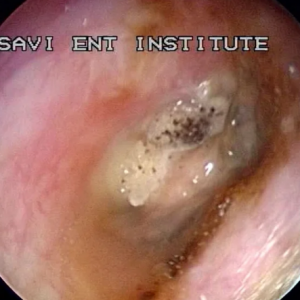
When It Comes To Ear Infections, Understanding Their Multifaceted Origins Is Pivotal. These Ailments, Often Characterized By Pain, Discomfort, And Potential Hearing Loss, Can Result From A Confluence Of Factors. This Article Delves Into The Intricate Web Of Causes Behind Ear Infections, Shedding Light On The Multifarious Elements That Contribute To These Troubling Conditions.
- Microbial Intruders
Ear Infections, Scientifically Referred To As Otitis, Frequently Occur Due To Microbial Invasions. Among These, The Most Common Culprits Are Bacteria And Viruses. The Ear, Particularly The Middle Ear, Is An Ideal Breeding Ground For These Microorganisms. Their Proliferation Can Cause Inflammation And, Subsequently, Infection. To Be More Precise, The Eustachian Tube, Responsible For Maintaining Ear Pressure Equilibrium, Can Become Blocked, Making It Easier For Pathogens To Infiltrate.
- Bacterial Blueprint
Bacterial Ear Infections, Termed Acute Otitis Media, Often Initiate From The Aftermath Of A Respiratory Tract Infection, Such As The Common Cold. These Infections Have A Predilection For The Middle Ear, Where The Accumulated Mucus Provides A Fertile Ground For Bacterial Colonization. Streptococcus Pneumoniae, Haemophilus Influenzae, And Moraxella Catarrhalis Are Some Of The Bacterial Players Behind These Scenarios. These Microbes, Guided By The Inscrutable Vagaries Of The Human Immune System, Can Trigger Inflammation And Lead To Discomfort And Pain.
- The Viral Vortex
Viruses Can Be Equally Culpable In Causing Ear Infections, A Condition Termed Viral Otitis Media. Often, Viral Infections In The Upper Respiratory Tract, Like The Flu Or The Common Cold, Serve As Precursors To Ear Infections. Rhinoviruses And Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Are Just A Couple Of Viral Agents That Can Sneak Their Way Into The Middle Ear. The Lining Of The Middle Ear Can Become Inflamed, And The Production Of Fluid Can Result In That Telltale Earache.
- Allergic Antagonism
Allergies, While Primarily Associated With Nasal Symptoms, Can Exert An Indirect Influence On Ear Infections. Allergic Reactions Can Cause Inflammation In The Upper Respiratory Tract, Leading To Nasal Congestion And Increased Mucus Production. As The Eustachian Tube Is Interconnected With The Nasal Passages, This Increased Mucus Can Impair Its Function, Subsequently Making The Middle Ear More Vulnerable To Infection.
- Anatomical Anomalies
In Some Individuals, The Ear Infection Causes Can Be Traced Back To The Unique Architecture Of Their Ears. Structural Anomalies, Such As A Particularly Narrow Eustachian Tube, Can Impede The
Normal Drainage Of Fluids From The Middle Ear. Consequently, Stagnant Fluid Provides An Ideal Environment For Bacteria To Thrive, Potentially Leading To Infection.
- Environmental Aggravators
Environmental Factors Also Play A Role In Ear Infection Causes. Exposure To Secondhand Smoke Or Air Pollutants Can Irritate The Respiratory Tract, Promoting Inflammation That Can Extend To The Middle Ear. Additionally, Changes In Atmospheric Pressure, Often Experienced During Air Travel Or Scuba Diving, Can Affect The Eustachian Tube's Functionality, Making It More Susceptible To Infection.
- Moisture Mischief
For Those Who Frequently Swim Or Partake In Water-Related Activities, Water Trapped In The Ear Can Be An Inadvertent Contributor To Ear Infections. The Persistent Dampness Creates A Hospitable Environment For Bacteria To Thrive. Known As Swimmer's Ear, This Condition Involves Infection Of The Ear Canal's Skin, Leading To Symptoms Like Itching, Redness, And Discomfort.
- Overzealous Ear Cleaning
Paradoxically, Maintaining Ear Hygiene Can Sometimes Backfire. Vigorous Or Improper Cleaning Methods, Such As The Insertion Of Cotton Swabs Or Other Objects Into The Ear Canal, Can Disrupt The Delicate Balance Of Earwax. In Doing So, It Can Inadvertently Push Earwax Deeper Into The Ear, Where It Can Accumulate And Potentially Become A Nidus For Infection.
- Immunological Imbalances
In Certain Instances, Underlying Health Conditions Can Exacerbate Susceptibility To Ear Infections. For Example, Individuals With Compromised Immune Systems, Such As Those With HIV/AIDS Or Autoimmune Diseases, May Be More Prone To Ear Infections Due To Their Diminished Ability To Combat Pathogens Effectively.
- Genetic Gambits
Although Relatively Rare, Genetic Predispositions Can Also Factor Into The Complex Equation Of Ear Infection Causes. Some Individuals Inherit Structural Ear Anomalies Or Immune System Deficiencies That Make Them More Vulnerable To Recurring Ear Infections.
- Age-Related Ailments
Age Is A Significant Determinant In The Propensity For Ear Infections. Infants And Young Children, Owing To Their Developing Eustachian Tubes And Immune Systems, Are Particularly Susceptible. Likewise, Older Adults May Also Face Increased Risk Due To Age-Related Changes In Ear Structure And Immune Function.
Ear Infection Causes Are Multifaceted, Stemming From An Interplay Of Factors Ranging From Microbial Invasions And Anatomical Peculiarities To Environmental Triggers And Immune System Dynamics. Recognizing These Underlying Causes Is Pivotal In Addressing And Preventing Ear Infections, Allowing For Timely Intervention And Effective Management Of This Often Painful And Bothersome Ailment. Ultimately, Awareness Of The Intricate Web Of Causes Empowers Individuals To Take Proactive Steps In Safeguarding Their Auditory Health And Well-Being.