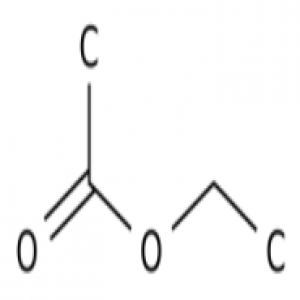
Sulfuric acid chemical formula is very reactive and dissolves most metals, it is a concentrated acid that oxidizes, dehydrates, or sulfonates most organic compounds, often causes charring.
Sulfuric acid chemical formula reacts violently with alcohol and water to release heat. It reacts with most metals, particularly when diluted with water, to form flammable hydrogen gas, which may create an explosion hazard. Sulfuric acid chemical formula is not combustible, but it is a strong oxidizer that enhances the combustion of other substances, does not burn itself. During fire, poisonous gases are emitted. Hazardous decomposition products are as follows: sulfur dioxide, sulfur trioxide, and sulfuric acid fumes.
Sulfuric acid chemical formula is a highly reactive chemical. It can react with cells and tissues upon contact. Damage caused by sulfuric acid can range from tissue irritation to chemical burns and necrosis. Signs and symptoms of exposure include tissue damage at point of contact. Tissue injury appears within seconds of exposure and can continue for hours and even days if not properly treated. The tissue damage extent and severity is dependent on the dose received, exposure interval, and strength (molar concentration) of the sulfuric acid solution. Highly concentrated sulfuric acid chemical formula solutions (usually found in industrial chemicals) are more dangerous than diluted acid solutions (as those found in consumer products).
The mode of action of sulfuric acid chemical formula is the same in humans and animals. Therefore, acute and chronic effects are expected to be the same for animals and humans.
Sulfuric acid chemical formula roasting and chlorination roasting are typical examples of salt roasting. The aim is to convert as many metallic sulfides or oxides in the material into soluble salts dissolved in water, or dilute acids, under controlled conditions. The main control conditions of sulfuric acid roasting are temperature and air volume. At the same temperature, the decomposition pressure and stability of various sulfates are different; the higher the temperature, the more unstable the sulfate is, and the easier it is to decompose into oxides. The selective sulfuric acid chemical formula roasting is carried out by controlling the temperature by the difference of sulfate stability. When the air volume can be the maximum value of the SO3 in the gaseous phase, it is the most suitable volume for sulfuric acid roasting. Sulfuric acid chemical formula roasting is applied to the treatment of copper concentrate, copper-cobalt concentrate, cobalt-sulfur concentrate and low-grade metal material. The fluidized roasting furnace is used for sulfuric acid chemical formula roasting in industry.
Sulfuric acid chemical formula has a very low vapor pressure and a lot of heat is released when it is mixed with water. Therefore, sulfuric acid chemical formula vapor can nucleate with water at very low concentrations, on the order of 108–1010 molecules per cubic centimeter, depending on temperature and relative humidity. This makes sulfuric acid chemical formula a candidate for forming new aerosol particles in the atmosphere, which has been known for a long time
Sulfuric acid chemical formula reacts violently with alcohol and water to release heat. It reacts with most metals, particularly when diluted with water, to form flammable hydrogen gas, which may create an explosion hazard. Sulfuric acid chemical formula is not combustible, but it is a strong oxidizer that enhances the combustion of other substances, does not burn itself. During fire, poisonous gases are emitted. Hazardous decomposition products are as follows: sulfur dioxide, sulfur trioxide, and sulfuric acid fumes.
Sulfuric acid chemical formula is a highly reactive chemical. It can react with cells and tissues upon contact. Damage caused by sulfuric acid can range from tissue irritation to chemical burns and necrosis. Signs and symptoms of exposure include tissue damage at point of contact. Tissue injury appears within seconds of exposure and can continue for hours and even days if not properly treated. The tissue damage extent and severity is dependent on the dose received, exposure interval, and strength (molar concentration) of the sulfuric acid solution. Highly concentrated sulfuric acid chemical formula solutions (usually found in industrial chemicals) are more dangerous than diluted acid solutions (as those found in consumer products).
The mode of action of sulfuric acid chemical formula is the same in humans and animals. Therefore, acute and chronic effects are expected to be the same for animals and humans.
Sulfuric acid chemical formula roasting and chlorination roasting are typical examples of salt roasting. The aim is to convert as many metallic sulfides or oxides in the material into soluble salts dissolved in water, or dilute acids, under controlled conditions. The main control conditions of sulfuric acid roasting are temperature and air volume. At the same temperature, the decomposition pressure and stability of various sulfates are different; the higher the temperature, the more unstable the sulfate is, and the easier it is to decompose into oxides. The selective sulfuric acid chemical formula roasting is carried out by controlling the temperature by the difference of sulfate stability. When the air volume can be the maximum value of the SO3 in the gaseous phase, it is the most suitable volume for sulfuric acid roasting. Sulfuric acid chemical formula roasting is applied to the treatment of copper concentrate, copper-cobalt concentrate, cobalt-sulfur concentrate and low-grade metal material. The fluidized roasting furnace is used for sulfuric acid chemical formula roasting in industry.
Sulfuric acid chemical formula has a very low vapor pressure and a lot of heat is released when it is mixed with water. Therefore, sulfuric acid chemical formula vapor can nucleate with water at very low concentrations, on the order of 108–1010 molecules per cubic centimeter, depending on temperature and relative humidity. This makes sulfuric acid chemical formula a candidate for forming new aerosol particles in the atmosphere, which has been known for a long time