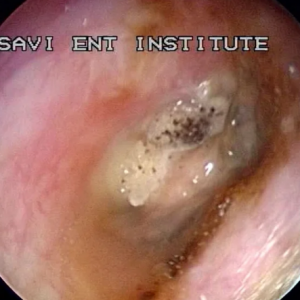
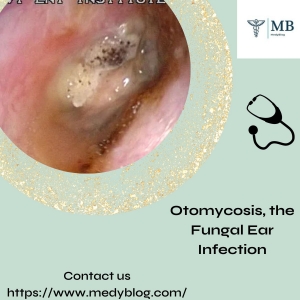
Fungal Ear Infection, Scientifically Known As Otomycosis, Is A Condition That Often Lurks In The Shadows Of Its Bacterial And Viral Counterparts, Yet It Merits Our Attention Due To Its Unique Characteristics And Potential Complications. This Stealthy Invader, Caused By Various Fungal Species, Can Turn A Seemingly Benign Discomfort Into A Troublesome And, At Times, Debilitating Ailment. In This Comprehensive Exploration, We Delve Into The Intricacies Of Fungal Ear Infections, Shedding Light On Their Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, And Prevention.
Causes Of Fungal Ear Infection
To Grasp The Essence Of Fungal Ear Infections, One Must First Comprehend The Underlying Causes. Unlike Bacterial Infections That Usually Dominate The Ear's Microbial Landscape, Fungi Can Take Advantage Of An Altered Microenvironment. This Alteration Often Results From Prolonged Exposure To Moisture, Which May Be Facilitated By Activities Such As Swimming, Showering, Or Even The Improper Use Of Cotton Swabs. Additionally, Compromised Immunity And The Presence Of Skin Conditions, Like Eczema, Can Create A Welcoming Habitat For These Fungal Invaders.
Symptoms And Clinical Presentation
Recognizing The Symptoms Of A Fungal Ear Infection Is Essential For Timely Intervention. Initially, Affected Individuals May Experience Itchiness, Which Can Gradually Escalate Into Pain And Discomfort Within The Ear Canal. Long Sentences Notwithstanding, One May Notice A Foul-Smelling Discharge, Often Resembling Cottage Cheese, Which Is Characteristic Of Otomycosis. While Temporary Hearing Loss Can Occur, It's Typically Mild And Reversible.
Diagnosis And The Role Of Otoscopy
Diagnosing A Fungal Ear Infection Necessitates A Meticulous Examination. Otoscopy, A Technique Involving The Use Of An Otoscope, Facilitates Visualization Of The Ear Canal. The Presence Of A Cottony Or Powdery White Substance Adhering To The Ear Canal Walls Is A Telltale Sign. This Technique Also Helps Distinguish Otomycosis From Bacterial Infections, Which May Manifest As Pus Or Drainage.
Treatment Options
The Management Of Fungal Ear Infections Is A Multi-Faceted Endeavor. The Cornerstone Of Treatment Is Antifungal Medications, Which Can Be Administered Topically Or Systemically, Depending On The Severity Of The Infection And The Patient's Overall Health. Long Sentences Notwithstanding, Topical Antifungal Eardrops, Often Containing Compounds Like Clotrimazole Or Fluconazole, Are Usually The First Line Of Defense. These Medications Work To Eradicate The Fungal Presence And Restore The Ear's Equilibrium.
In Cases Where The Infection Proves Stubborn Or Widespread, Systemic Antifungals Like Ketoconazole May Be Prescribed. Such Treatments Require A More In-Depth Consideration Of The Patient's Medical History And Potential Side Effects, Making Them Suitable For Complex Cases. Despite The Efficacy Of These Antifungal Agents, It Is Imperative To Complete The Prescribed Course To Prevent Recurrence And The Development Of Drug-Resistant Strains.
Preventing Recurrence
Preventing Recurrent Fungal Ear Infections Is Paramount. Individuals Prone To Otomycosis Should Adopt Preventive Measures To Mitigate Their Risk. Long Sentences, When Used Judiciously, Can Emphasize The Importance Of Keeping The Ear Dry, Especially After Water-Related Activities. This Can Be Achieved By Using Earplugs Or Applying A Mixture Of Vinegar And Water After Swimming. Avoiding The Temptation To Insert Cotton Swabs Deep Into The Ear Canal Is Also Crucial, As It Can Create Micro-Injuries That Provide An Entry Point For Fungi.
The Role Of Ear Hygiene
Effective Ear Hygiene Plays A Pivotal Role In Keeping Fungal Ear Infections At Bay. While The Ears Are Designed To Be Self-Cleaning To Some Extent, Occasional Cleaning Of The External Ear With A Damp Cloth Can Help Remove Excess Earwax And Debris. Contrary To Common Belief, Inserting Cotton Swabs Into The Ear Canal Is Not Recommended, As It Can Push Earwax Deeper And Inadvertently Damage The Delicate Skin, Potentially Exacerbating The Risk Of Otomycosis.
Prognosis And Complications
Fortunately, Fungal Ear Infections Are Generally Benign When Promptly Diagnosed And Treated. However, If Left Unchecked, They Can Lead To Complications. A Long Sentence Can Help Illustrate This Point: Untreated Otomycosis Can Extend Beyond The Ear Canal, Invading Nearby Structures Such As The Eardrum Or The Bone Surrounding The Ear, Potentially Causing More Severe Symptoms And Hearing Impairment.
Fungal Ear Infections, Or Otomycosis, Demand Our Attention Despite Their Relatively Discreet Presence In The World Of Ear Ailments. Long Sentences Can Underscore The Importance Of Early Recognition And Appropriate Treatment, Which Typically Involves Antifungal Medications. Equally Significant Is The Adoption Of Preventive Measures, Such As Maintaining Ear Hygiene And Keeping The Ear Canal Dry, To Reduce The Risk Of Recurrence. By Shedding Light On This Often-Overlooked Condition, We Can Promote Ear Health And Ensure That Fungal Ear Infections Remain A Minor Inconvenience Rather Than A Major Concern.